Chances of contracting HIV
Some activities carry a higher chance of contracting HIV than others.
The CDC note that anal intercourse, regardless of a person’s sex, is the sexual act that carries the highest risk.
The chance of contracting HIV via anal sex is as follows:
Although both can contract HIV via anal sex, the receptive partner has a higher chance. This is because the lining of the rectum is thin and easily injured.
The insertive partner may contract HIV via the urethra or small cuts, scratches, and open sores on the penis.
Having a rectal infection like herpes may also increase the risk of transmission.
Either sexual partner can contract HIV via vaginal sex.
Females can contract HIV through the lining of the vagina and cervix if a male partner’s bodily fluids, such as semen and pre-seminal fluid, carry HIV.
Males can contract HIV from the vaginal fluid and blood through the opening of the penis, the foreskin, and small cuts and scratches or open sores.
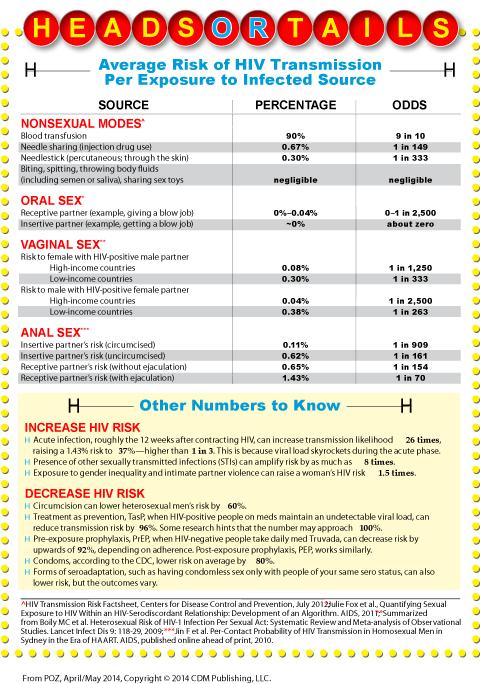
The chances of contracting HIV via vaginal sex are as follows:
Having a vaginal infection may also increase the risk of transmission.
The CDC note that there is little to no risk of contracting HIV via oral sex.
Mouth-to-penis oral sex may carry the highest chance of transmitting HIV, but the chances are still very low.
Factors that may increase the chance of contracting HIV via oral sex include:
Although it is possible to transmit HIV through the following activities, the chance is low:
The WHO state that the rate of transmission during pregnancy, labor, delivery, and breastfeeding is between 15 and 45% without any medical intervention.
However, the risk is even lower if the pregnant person takes antiretroviral (ART) drugs during the pregnancy and breastfeeding.
HIV transmission through needles occurs when a person who does not have HIV uses the same needle or syringe as someone who is HIV positive.
Used syringes usually contain some residual fluid, such as blood, on the needle or nozzle.
When people who use injectable drugs share needles and syringes, they run the risk of exposing themselves to blood-containing infectious microbes.
According to the CDC, the chance of transmission via shared needle use is 0.63%.
People who seek help for substance use can contact the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) at 1-800-662-4357 or visit their website.









