NHS GP and chief medical Officer at Push DoctorA urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection in any part of your urinary system. This includes your kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Most commonly, however, UTIs affect just the bladder and urethra. Urinary tract infections typically occur when bacteria enters the urinary tract through the urethra and begin to multiply in the bladder.
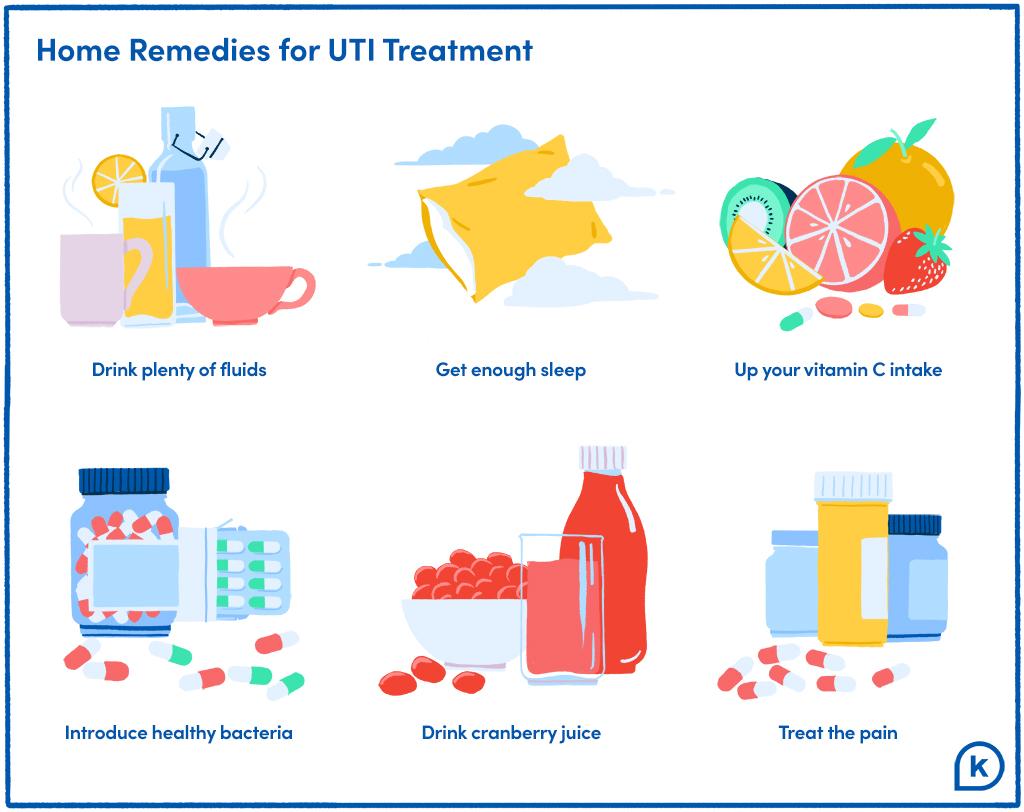
Keeping hydrated will dilute your urine and ensure that you go to the toilet more frequently. This allows bacteria in the urinary tract to be flushed out before an infection can develop. If you are a caregiver, ensure that nappies and incontinence pads are changed quickly after they are soiled. Keep the genital area dry and clean, but avoid potentially irritating “hygiene”
Sponsored